
Here's how I'd do it: import numpy as npį = sp.interpolate. That being said, 'linear' is the default interpolation method for interp1, so you can also simply leave that argument out and use the command: interp1(TMP.time_hor, TMP.lane_hor, TMP.travel_time)Įdit: I just realized what you were asking was backwards you want to interpolate using the 'next' method in Python instead. Looking at NumPy's documentation ( ), it appears as though they use linear interpolation, so if you want the same output, you just need to specify this in your MATLAB command, like this: interp1(TMP.time_hor, TMP.lane_hor, TMP.travel_time, 'linear') The interpolation method 'next' interpolates to the next data point in the data set (see: ). (The default is 'linear' so I assume the same extrapolation method.) Of course, always be careful about.
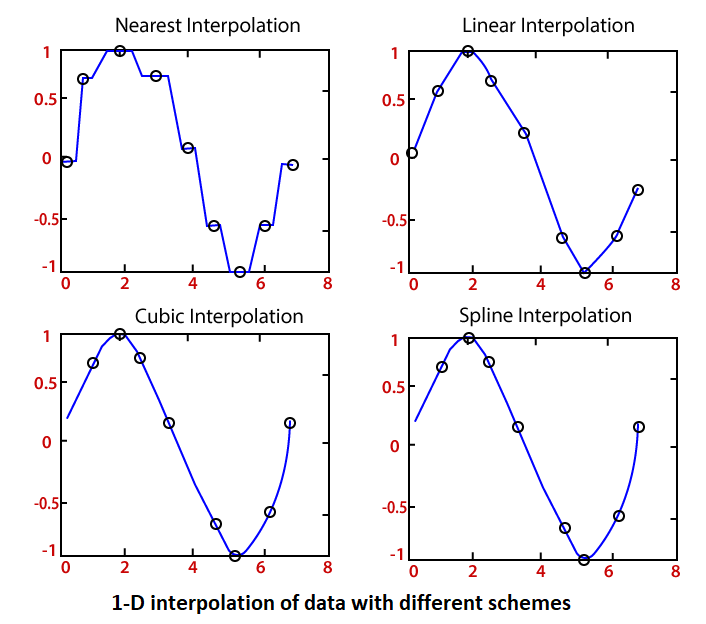
interpco2 interp1 (cleantimeco2, cleanco2, timecommon, 'linear','extrap') Choose the appropriate interpolation method. de Boor, C., A Practical Guide to Splines, Springer-Verlag, 1978.Which interpolation is meant by 'next'? Usually by default is linear. Answers (1) It will do that if you atempt to extrapolate without telling interp1 how you want to do it. Interpft, interp2, interp3, interpn, pchip, spline See the pchip reference page for more information. This method preserves monotonicity and the shape of the data. For access to more advanced features, see the spline reference page, the M-file help for these functions, and the Spline Toolbox.įor the ' pchip' and 'cubic' methods, interp1 calls a function pchip that performs piecewise cubic interpolation within the vectors x and y. spline uses them to perform the cubic spline interpolation. These routines form a small suite of functions for working with piecewise polynomials. The ' nearest' and ' linear' methods have straightforward implementations.įor the ' spline' method, interp1 calls a function spline that uses the functions ppval, mkpp, and unmkpp. Then the population in 1975, obtained by table lookup within the matrix tab, is If a portion of the census data is stored in a single 5-by-2 table,

Sometimes it is more convenient to think of interpolation in table lookup terms, where the data are stored in a single table. Now interpolate within the data at every year from 1900 to 2000, and plot the result. The expression interp1(t,p,1975) interpolates within the census data to estimate the population in 1975. P = Here are two vectors representing the census years from 1900 to 1990 and the corresponding United States population in millions of people. Generate a coarse sine curve and interpolate over a finer abscissa.Įxample 2. Type help interp1q at the command line for more information.Įxample 1. The step size I want is frequency(size 101) and the array is reffft. For interp1q to work properly, x must be a monotonically increasing column vector and Y must be a column vector or matrix with length(X) rows. Im trying to interpolate an array of size nearly 2000. Note interp1q is quicker than interp1 on non-uniformly spaced data because it does no input checking. Described in table lookup terms, the table is and interp1 looks up the elements of xi in x, and, based upon their locations, returns values yi interpolated within the elements of Y. Interpolation is the same operation as table lookup. This function is shown below, along with the relationship between vectors x, Y, xi, and yi. It finds values at intermediate points, of a one-dimensional function that underlies the data. If you have multiple sets of data that are sampled at the same point. Vector xq contains the coordinates of the query points.
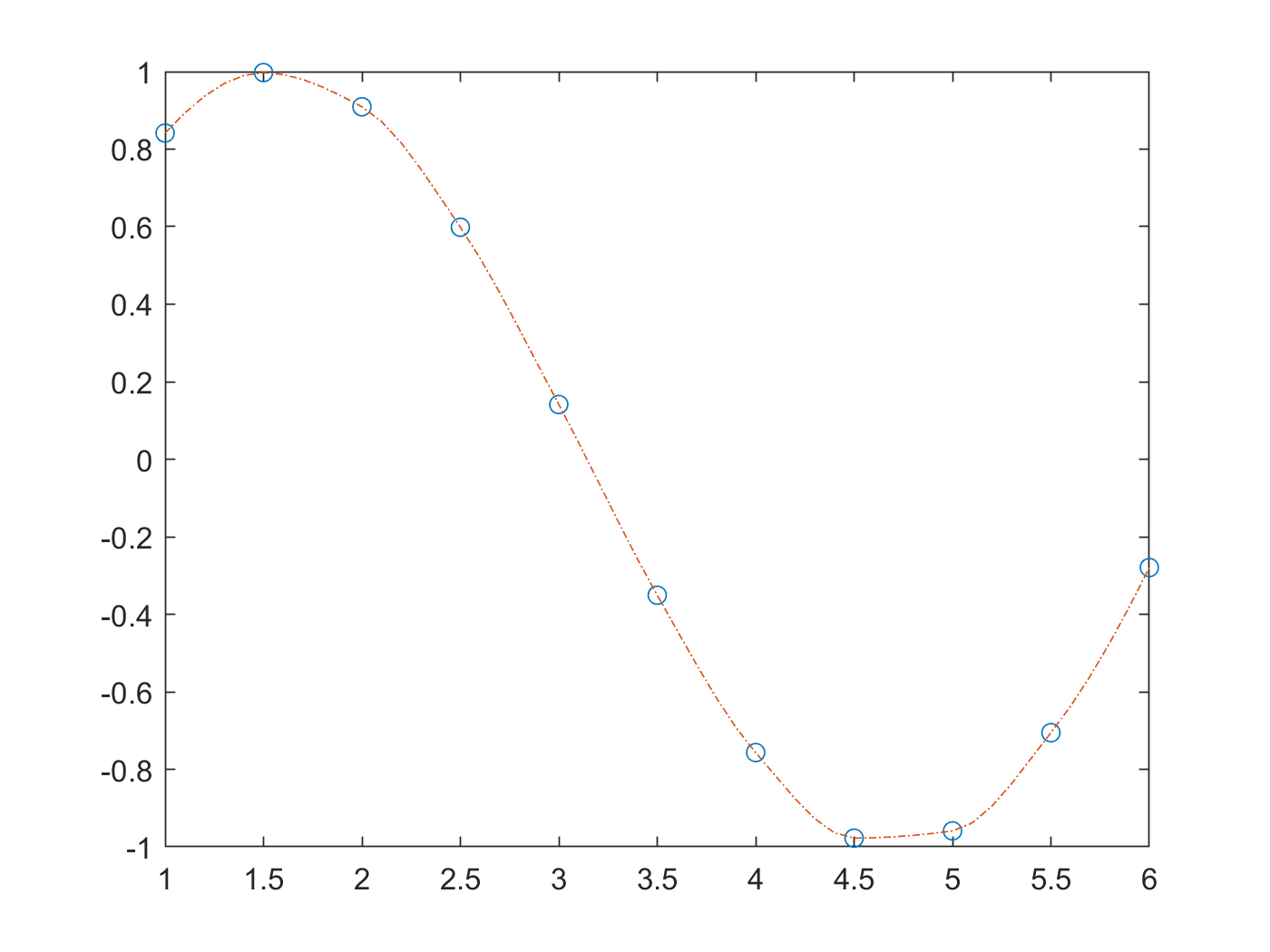
Vector x contains the sample points, and v contains the corresponding values, v ( x ). The interp1 command interpolates between data points. vq interp1 (x,v,xq) returns interpolated values of a 1-D function at specific query points using linear interpolation. Returns the scalar extrapval for out of range values. Uses the specified method to perform extrapolation for out of range values. (Originally posted on Doug's MATLAB Video Tutorials blog.) This short video shows how you can take a sparsely sampled sine wave. For all other methods, interp1 performs extrapolation for out of range values. If Y is a matrix, then the interpolation is performed for each column of Y and yi is length(xi)-by- size(Y,2).Īssumes that x = 1:N, where N is the length of Y for vector Y, or size(Y,1) for matrix Y.įor the 'nearest', 'linear', and 'v5cubic' methods, interp1(x,Y,xi,method) returns NaN for any element of xi that is outside the interval spanned by x. The vector x specifies the points at which the data Y is given.

Returns vector yi containing elements corresponding to the elements of xi and determined by interpolation within vectors x and Y. One-dimensional data interpolation (table lookup) Interp1 (MATLAB Functions) MATLAB Function Reference


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
